Power plants on municipal solid waste (MSW) using the Brayton cycle. Serial production of “NEUTRON-GTES” with an electrical capacity ranging from 1.35 MW to 28 MW.
Today, the challenge of ensuring environmental safety faces the following problems:
Waste has potential energy, raw material, and economic value. To solve the task of creating equipment that allows for environmentally friendly waste disposal and recycling while using them rationally as resources, “UGK Energetika” offers the following solutions:
Incineration
Organized controlled combustion with access to oxygen. The most applied, energy-efficient method of waste disposal. End products of direct incineration are ash and significant volumes of toxic substances released into the environment.
Pyrolysis
Decomposition of organic matter into lighter molecules or elements under increased temperature without access to oxygen.
Plasma Technologies
High-temperature thermal decomposition of particularly hazardous waste at temperatures ranging from 1300 to 3000°C.
A combination of technologies is necessary for effective and environmentally friendly solutions.
Effective and Environmentally Friendly Disposal
Should be based on deep processing with the sequential neutralization of toxic components.
Plasma Gasification Plants for Environmentally Friendly Waste Disposal
Plasma gasification is a proven advanced technology for the disposal of unsorted waste and is the most environmentally safe method.
A combination of technologies for a single solution: incineration and high-temperature afterburning technologies, final gas purification systems, heat and power generation.
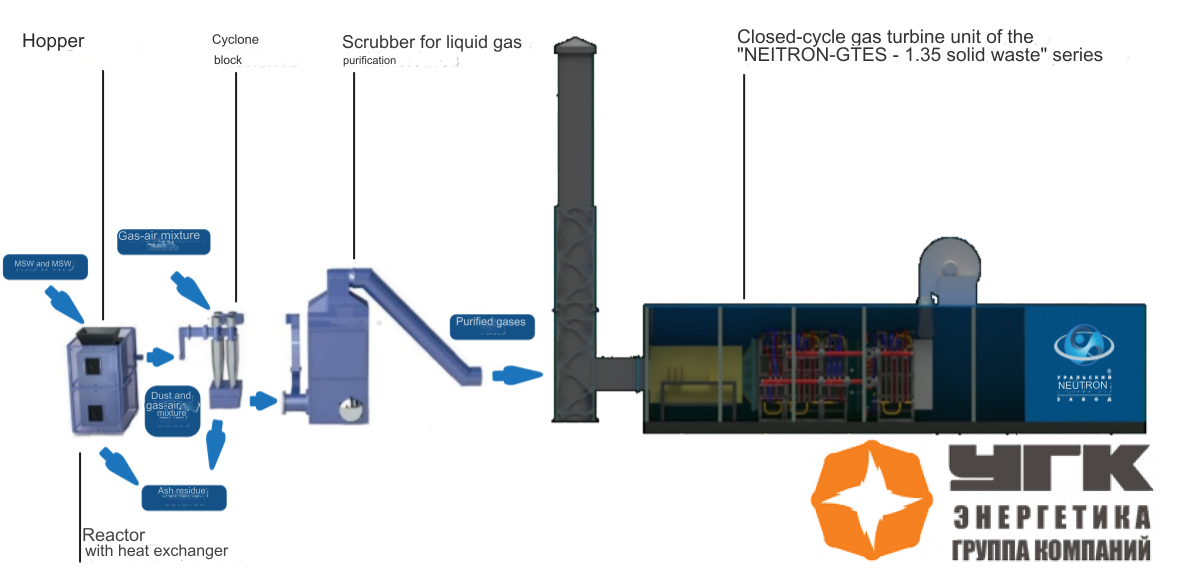
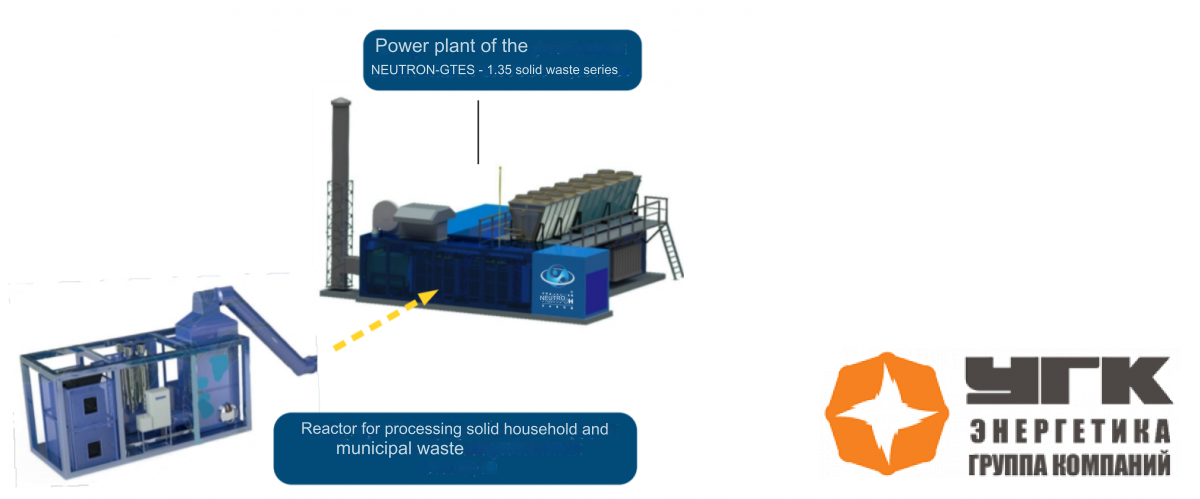 Technological Scheme of the Mobile MSW Processing Complex
Technological Scheme of the Mobile MSW Processing Complex
Complex Advantages
Thanks to its mobility and fuel flexibility, the complex is successfully used:
Description of the “NEUTRON-GTES – 1.35 MSW” Power Plant Series
The NEUTRON-GTES power plant operates on the closed Brayton cycle principle. The working fluid of the plant is carbon dioxide (CO2) in a subcritical state. The working fluid heated in the PRT by technological process heat enters the turbine inlet, converting thermal energy into mechanical energy. As a result, torque is generated, driving the turbocompressor and electric generator mounted on a single shaft. After the turbine, the working fluid, through heat exchangers and a two-stage compressor, is fed back into the PRT inlet, and the cycle repeats.
To apply for a mini-CHP with MSW processing, you need to fill out an online survey form.
For all questions, please contact our specialists:
| Yekaterinburg | Russia, CIS | |
| +7 (343) 272-31-80 | 8 (800) 201-71-60 | ka@urgk.ru |
| +7 (343) 272-31-82 | office@urgk.ru |